

05 Oct, 2022
Cellulite is a perplexing issue for women of all ages, sizes, and ethnic backgrounds. With 80 percent of women over the age of 20 having cellulite, even if it's slight, you're in the vast majority. Even though cellulite is a common and mostly harmless condition, it can be tough to deal with emotionally and physically. If you're one of the many people who are unhappy with their appearance because of cellulite, don't despair. There are things you can do to improve your situation. Cellulite doesn't have to ruin your life. With a little effort, you can feel better about yourself. What is Cellulite?
06 Sep, 2022
Do you know the difference between brown fat, white fat, and beige fat? If not, don't worry – most people don't. But understanding the difference is important if you're trying to lose weight. In this blog post, we will discuss the three different types of fat and how they impact weight loss. We'll also provide tips on how to activate your brown fat and burn more calories!
22 Aug, 2022
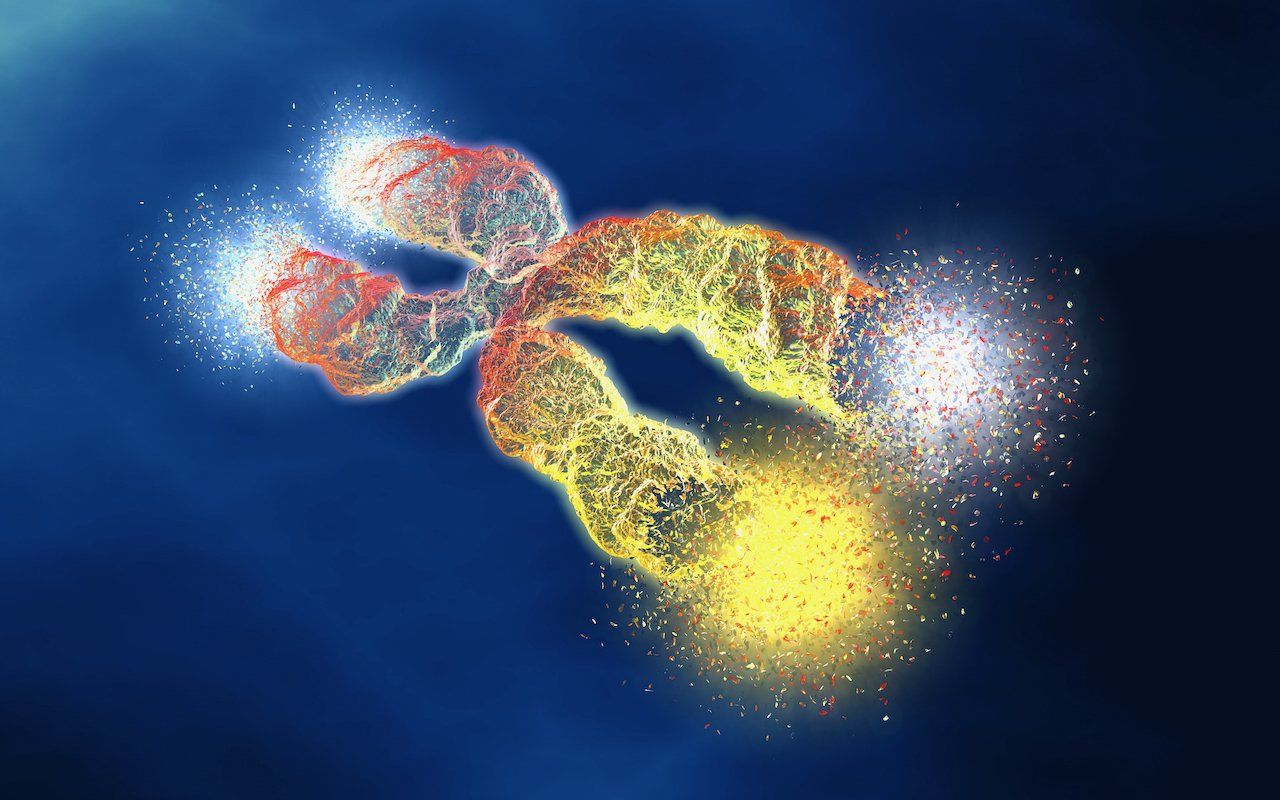
It's not a surprise to anyone that we all want to prevent aging. Now, new research suggests that our telomeres may play a role in how quickly we age. What are telomeres, you ask? They are the protective caps on the ends of our chromosomes, and they play an important role in aging. The length of our telomeres has been shown to predict lifespan, so it's no wonder that scientists are interested in understanding more about them! In this blog post, we will explore the latest research on telomeres and aging. Stay tuned for exciting updates! What are telomeres? Telomeres are tiny caps of DNA at the end of chromosomes and their main function is to protect the chromosome from DNA damage much like our shoelaces have aglets (or plastic tips) to prevent the shoelace from fraying. Chromosomes contain our DNA and our DNA is what makes us who we are. Telomeres prevent our DNA from being damaged or lost as cells divide. However, telomeres get shorter with each cell division. When they are too short, the cell is no longer able to divide and dies. This is how we age. But what if we could lengthen our telomeres, and in turn, reverse aging? According to new research, it might be possible.
12 Aug, 2022
Functional Medicine is becoming more and more popular, and for good reason! This type of medicine focuses on identifying and addressing the root causes of disease, rather than just treating the symptoms. If you are looking for an alternative to traditional medicine, or if you are struggling with a chronic health condition, functional medicine may be the right choice for you. In this blog post, we will discuss the top 10 reasons everyone should see a Functional Medicine provider. Functional Medicine is a personalized, whole-person approach to health care. Rather than simply treating the symptoms of disease, Functional Medicine providers work to identify and address the underlying causes of illness. This holistic approach often leads to better health outcomes and improved quality of life for patients. There are many reasons why someone might choose to see a Functional Medicine provider. Here are the top ten reasons: -Functional Medicine providers focus on prevention. By identifying and addressing the root causes of disease, Functional Medicine providers can help prevent illness before it starts. This is a key difference between traditional and Functional Medicine approaches. Traditional medicine often focuses on treating illness after it has already developed, while Functional Medicine works to prevent illness from occurring in the first place. -Functional Medicine providers take a holistic approach. Functional Medicine providers view each patient as a unique individual, rather than just a collection of symptoms. This means that they take into account a wide range of factors when developing a treatment plan, including lifestyle, diet, and environmental factors. This holistic approach often leads to better health outcomes and improved quality of life for patients. -Functional Medicine providers treat the whole person, not just the symptoms. Traditional medicine often focuses on treating the symptoms of disease, rather than the underlying causes. This can lead to a never-ending cycle of symptom management, rather than true healing. Functional Medicine providers, on the other hand, focus on treating the whole person. By addressing the underlying causes of disease, they can help patients achieve lasting health and wellness. -Functional Medicine providers use a systems-based approach. Functional medicine providers understand that the human body is a complex system, made up of interconnected systems. This systems-based approach leads to a more comprehensive understanding of each patient’s unique health needs. -Functional Medicine providers individualize treatment plans. Because each person is unique, functional medicine providers tailor treatment plans to meet the specific needs of each patient. This personalized approach often leads to better health outcomes and improved quality of life. -Functional Medicine providers use evidence-based treatments. Functional Medicine providers use a variety of evidence-based treatments, including diet, lifestyle changes, and supplements. It also considers the dynamic balance of gene-environment interactions.This scientific approach leads to more effective and sustainable results. -Functional Medicine providers are trained in both traditional and alternative therapies. Functional Medicine providers are often trained in both traditional and alternative therapies. This allows them to offer a more comprehensive approach to care. -Functional Medicine providers work with you to develop a treatment plan. Functional Medicine providers work with you to develop a treatment plan that meets your specific needs and goals. Because Functional Medicine is preventative, integrative, and personalized it often leads to better health outcomes and improved quality of life for patients. -Functional Medicine providers use Practitioner-Grade supplements Functional Medicine providers use high-quality and purity, Practitioner-Grade supplements to support their patients. This ensures that patients are getting the best possible care. -Functional Medicine is an emerging field. Functional Medicine is an emerging field of medicine that is still evolving. This means that there is a lot of potential for new and innovative treatments. As more research is conducted, the potential benefits of functional medicine will become even more clear. If you’re looking for a more comprehensive approach to your health care, a Functional Medicine provider may be right for you. Contact a Functional Medicine (LINK: https://www.drmichaelswellness.com) provider today to learn more about how this unique approach to care can help you achieve lasting health and wellness. If you want to learn more about Functional Medicine and Genomics check out my new book "Understanding Genomics; How Nutrition, Supplements, and Lifestyle Can Help You Unlock Your Genetic Superpowers." This book is a must-read if you want to learn how to control your genetic destiny! Order a copy today ! Until then, stay healthy and happy! Dr. Marios Michael https://www.drmichaelswellness.com Resources: Dr. Marios Michael, DC, CNS, cFMP, 06/2022, Understanding Genomics; How Nutrition, Supplements, and Lifestyle Can Help You Unlock Your Genetic Superpowers, 1st edition, Austin, Bookbaby. Bland J. Defining Function in the Functional Medicine Model. Integr Med (Encinitas). 2017 Feb;16(1):22-25. PMID: 28223904; PMCID: PMC5312741. Jones DS, Quinn S. Textbook of Functional Medicine. Gig Harbor, WA: Institute for Functional Medicine; 2010. Bland J. Functional Medicine: An Operating System for Integrative Medicine. Integr Med (Encinitas). 2015 Oct;14(5):18-20. PMID: 26770161; PMCID: PMC4712869. Beidelschies M, Alejandro-Rodriguez M, Guo N, et alPatient outcomes and costs associated with functional medicine-based care in a shared versus individual setting for patients with chronic conditions: a retrospective cohort studyBMJ Open 2021;11:e048294. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-048294 Droz N, Hanaway P, Hyman M, Jin Y, Beidelschies M, Husni ME (2020) The impact of functional medicine on patient-reported outcomes in inflammatory arthritis: A retrospective study. PLoS ONE 15(10): e0240416. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240416 Medical Disclaimer: The information included on this blog is for educational purposes only. It is not intended nor implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice. The reader should always consult his or her healthcare provider to determine the appropriateness of the information for their own situation or if they have any questions regarding a medical condition or treatment plan. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this blog! Reading the information on this blog does not create a physician-patient relationship. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.

08 Aug, 2022
Did you know that your gut health affects your mindset? When our gut is healthy, we tend to be happier and more positive. But when our gut is unhealthy, we can experience a lot of negative emotions like anxiety and depression. In this blog post, we will discuss the connection between gut health and mindset, and how you can improve both by making some simple changes to your diet and lifestyle. The gut-brain axis So how exactly does gut health affect mental health? Well, it all starts with the gut-brain axis. This is a bidirectional communication system that allows information to be passed between the gut and the brain. The gut-brain axis is made up of the nervous system, the endocrine system, the immune system, and the gut microbiome. These systems work together to regulate mood, anxiety, immunity, and stress levels. The gut microbiota has been shown to influence the gut-brain axis. The microbiome is composed of trillions of microbes, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. These microbes are essential for gut health and have a profound impact on the gut-brain axis. The gut microbiome influences the development and function of the brain, and the brain influences the composition of the gut microbiome. For example, gut bacteria can produce neurotransmitters that affect the brain. They can also alter the way the body responds to stress hormones. These changes can then lead to changes in mood and behavior. Psychobiotics! There is a growing body of evidence to suggest that gut health plays a role in mental health. For example, studies have shown that probiotics can improve mood and cognitive function. Probiotics are live microorganisms that have a beneficial effect on gut health. Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Bifidobacterium adolescentis for example are probiotic strains that can produce the neurotransmitter GABA. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that connect nerve cells. Serotonin, dopamine, and GABA are examples of neurotransmitters. GABA helps to regulate brain activity and can calm anxiety. The researchers found that the mice that consumed these probiotics had changes in their brain chemistry. The levels of GABA were increased and the mice were more relaxed. The Vagus Nerve The microbiota, the gut, and the brain communicate through the microbiota-gut-brain axis in both directions via the autonomic nervous system. The vagus nerve, the principal component of the parasympathetic nervous system, is a mixed nerve composed of 80% input sensory fibers (transmitting signals to the central nervous system) and 20% output motor fibers (transmitting signals in the opposite direction). It runs from the stomach to the brain and connects us to our emotions. This nerve is involved in gut-brain communication and has a significant impact on our mood. The vagus nerve sends messages directly from the gut to the brain. This nerve controls messages to the gut as well as other vital organs, like the heart and lungs. Gut health So, what is gut health? Gut health is the condition of our digestive system. This includes the stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and other organs like the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. There are more than five hundred distinct species of bacteria in the gut, and it is home to trillions of microorganisms. These gut bacteria are essential for gut health. They help us digest food, absorb nutrients, and produce vitamins and minerals. Gut bacteria also play a role in immunity, inflammation, and the development of the gut-brain axis. Studies have shown that gut health is linked to our DNA. Gut bacteria can affect the expression of our genes! Microbiomes can influence which genes are turned on or off, amplified, or silenced. Because our DNA is the blueprint for life, our gut health can have a significant impact on our mood, actions, and even thoughts. So how can we improve our gut health? When we think about gut health, we often think about the bacteria in our gut. But our gut health is also influenced by the foods we eat, the stress we experience, and the toxins we're exposed to. All of these factors can impact our gut microbiome, which in turn can influence our mood and mental health. There are a few simple things you can do: -Eat more fiber. Fiber is essential for gut health, as it helps keep our digestive system moving smoothly. Foods high in fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. -Cut out processed foods. Processed foods are full of sugar and unhealthy fats that can damage gut bacteria. Instead, opt for fresh, whole foods that are easy on the digestive system. -Get enough sleep. Sleep is important for gut health, as it allows our bodies to repair and regenerate. Make sure to get at least seven hours of sleep each night. -Reduce stress. Stress can damage gut bacteria, affect gut motility and increase gut permeability, which can lead to inflammation. Try to relax with some deep breathing or meditation. -Avoid a diet consisting of large amounts of sugar and fat because it affects neurotransmitter metabolism and subsequently brain function by altering the gut microbiota. Studies have shown that gut microbiota composition is different between people with depression and those without. -Take Practitioner-Grade Prebiotic (LINK:https://mmichael.metagenics.com/item/bundlpztpmxy/pre-biotics/1-practitioner.html) and Probiotic (LINK: https://mmichael.metagenics.com/item/bund3j8jntcb/spectrum/1-practitioner.html) Supplements. -Eat probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, and kimchi. -Exercise regularly. -Consuming prebiotic-rich foods like garlic, onions, bananas, and oats can also help feed the good bacteria in your gut. -A 10-day detox ( LINK:https://mmichael.metagenics.com/item/bundxbphxglh/detox-10-days/1-practitioner.html) or a 28-day detox (LINK: https://mmichael.metagenics.com/item/bundud3nic3i/detox-28-days/1-practitioner.html) is recommended. Toxins can cause havoc and disrupt the beneficial gut flora. Try doing a cleanse or detox once or twice per year to help keep your gut healthy and balanced. key points Gut cells outnumber human cells ten to one. The gut microbiome contains over 100 trillion microorganisms and over 500 different species of bacteria. The gut has been nicknamed the "second brain". There is a gut-brain connection and it's a two-way street. Gut bacteria can influence the way we think and feel. Changes in gut health can lead to changes in mood and behavior. Prebiotics and probiotics have the potential to enhance gut health and mental well-being. You can improve your gut health by eating a healthy diet, exercising, detoxing, and managing stress levels. Conclusion The connection between gut health and mental health is complex, and more research is needed to understand the full extent of the gut-brain axis. However, the growing body of evidence suggests that gut health plays an important role in mental health. So next time you're feeling down, try reaching for a probiotic-rich food or supplement instead of unhealthy comfort foods. Your gut (and mind) will thank you! If you are struggling with gut issues or mental health issues, please reach out to a qualified healthcare professional or a Functional Medicine Practitioner (LINK https://www.drmichaelswellness.com) to help you. If you'd like to learn more about gut health, I highly recommend my new book, "Understanding Genomics; How Nutrition, Supplements, and Lifestyle Can Help You Unlock Your Genetic Superpowers". This book is a must-read if you want to learn how to control your genetic destiny! Order a copy today ! Until then, stay healthy and happy! Dr. Marios Michael https://www.drmichaelswellness.com Resources: Dr. Marios Michael, DC, CNS, cFMP, 06/2022, Understanding Genomics; How Nutrition, Supplements, and Lifestyle Can Help You Unlock Your Genetic Superpowers, 1st edition, Austin, Bookbaby. Xu H, Liu M, Cao J, Li X, Fan D, Xia Y, Lu X, Li J, Ju D, Zhao H. The Dynamic Interplay between the Gut Microbiota and Autoimmune Diseases. J Immunol Res. 2019 Oct 27;2019:7546047. doi: 10.1155/2019/7546047. PMID: 31772949; PMCID: PMC6854958. Álvarez-Arraño V, Martín-Peláez S. Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics on Weight Loss in Subjects with Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2021 Oct 17;13(10):3627. doi: 10.3390/nu13103627. PMID: 34684633; PMCID: PMC8540110. Clapp M, Aurora N, Herrera L, Bhatia M, Wilen E, Wakefield S. Gut microbiota's effect on mental health: The gut-brain axis. Clin Pract. 2017 Sep 15;7(4):987. doi: 10.4081/cp.2017.987. PMID: 29071061; PMCID: PMC5641835. He Song, Li Hao, Yu Zehui, Zhang Faming, Liang Sicheng, Liu Hang, Chen Hongwei, Lü MuHan. The Gut Microbiome and Sex Hormone-Related Diseases. Frontiers in Microbiology.Vol. 12 2021. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2021.711137 Tang WH, Kitai T, Hazen SL. Gut Microbiota in Cardiovascular Health and Disease. Circ Res. 2017 Mar 31;120(7):1183-1196. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.309715. PMID: 28360349; PMCID: PMC5390330. Vivarelli S, Salemi R, Candido S, Falzone L, Santagati M, Stefani S, Torino F, Banna GL, Tonini G, Libra M. Gut Microbiota and Cancer: From Pathogenesis to Therapy. Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jan 3;11(1):38. doi: 10.3390/cancers11010038. PMID: 30609850; PMCID: PMC6356461. Fujimura KE, Lynch SV. Microbiota in allergy and asthma and the emerging relationship with the gut microbiome. Cell Host Microbe. 2015 May 13;17(5):592-602. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.04.007. PMID: 25974301; PMCID: PMC4443817. Nagao-Kitamoto H, Kitamoto S, Kuffa P, Kamada N. Pathogenic role of the gut microbiota in gastrointestinal diseases. Intest Res. 2016 Apr;14(2):127-38. doi: 10.5217/ir.2016.14.2.127. Epub 2016 Apr 27. PMID: 27175113; PMCID: PMC4863046. Wang R, Tang R, Li B, et al. Gut microbiome, liver immunology, and liver diseases. Cell Mol Immunol 2021;18(1):4-17. Medical Disclaimer: The information included on this blog is for educational purposes only. It is not intended nor implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice. The reader should always consult his or her healthcare provider to determine the appropriateness of the information for their own situation or if they have any questions regarding a medical condition or treatment plan. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this blog! Reading the information on this blog does not create a physician-patient relationship. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
05 Aug, 2022
Your gut health is extremely important, and when it is imbalanced, it can lead to several health conditions. In this blog post, we will discuss 15 health conditions that are linked to an imbalanced microbiome. We will also provide tips on how you can restore balance in your gut and improve your overall health! We all know how important gut health is for our general health, but did you know that an imbalanced microbiota might cause a slew of illnesses? Here are 15 conditions that have been linked to an imbalanced microbiome: Allergies and asthma Autoimmune diseases Cancer Cardiovascular disease Depression and anxiety Digestive disorders: irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Eczema, acne, and psoriasis Fatigue syndrome Hormonal imbalances: Infertility and PCOS Insulin resistance and type II diabetes Migraines and headaches Neurodegenerative diseases: Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Obesity Recommendations There are a few things you can do to restore balance in your gut and improve your overall health. First, focus on eating a nutrient-dense diet that includes plenty of fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. The Mediterranean diet is particularly beneficial for gut health. Second, make sure to get enough high-quality probiotics, prebiotics, and fermented foods. Probiotics are live bacteria that can help restore balance to your gut. Prebiotics are indigestible fibers that act as food for probiotics. Fermented foods are a great source of both probiotics and prebiotics. Third, eliminating processed foods, sugars, and other inflammatory foods that can trigger an imbalance in gut bacteria. Keeping a daily food diary can help identify food sensitivities. Fourth, avoiding antibiotics when possible is also key, as they can kill both good and bad bacteria in your gut. If you must take them, make sure to supplement with probiotics to help restore balance. Always consult with your healthcare practitioner before stopping or starting any medications. Finally, make sure to get enough sleep and manage stress levels as both can hurt gut health. By following these tips, you can help restore balance in your gut and improve your overall health! If you are struggling with any chronic health conditions, work with a Functional Medicine Practitioner to find the best treatment plan for you. If you'd like to learn more about autoimmune diseases, gut health, and Genomics, I've just released a book entitled " Understanding Genomics : How Nutrition, Supplements, and Lifestyle Can Help You Unlock Your Genetic Superpowers." This book is a must-read if you want to learn how to control your genetic destiny! Order a copy today ! Until then, stay healthy and happy! Dr. Marios Michael https://www.drmichaelswellness.com Resources: Dr. Marios Michael, DC, CNS, cFMP, 06/2022, Understanding Genomics; How Nutrition, Supplements, and Lifestyle Can Help You Unlock Your Genetic Superpowers, 1st edition, Austin, Bookbaby. Xu H, Liu M, Cao J, Li X, Fan D, Xia Y, Lu X, Li J, Ju D, Zhao H. The Dynamic Interplay between the Gut Microbiota and Autoimmune Diseases. J Immunol Res. 2019 Oct 27;2019:7546047. doi: 10.1155/2019/7546047. PMID: 31772949; PMCID: PMC6854958. Álvarez-Arraño V, Martín-Peláez S. Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics on Weight Loss in Subjects with Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2021 Oct 17;13(10):3627. doi: 10.3390/nu13103627. PMID: 34684633; PMCID: PMC8540110. Clapp M, Aurora N, Herrera L, Bhatia M, Wilen E, Wakefield S. Gut microbiota's effect on mental health: The gut-brain axis. Clin Pract. 2017 Sep 15;7(4):987. doi: 10.4081/cp.2017.987. PMID: 29071061; PMCID: PMC5641835. He Song, Li Hao, Yu Zehui, Zhang Faming, Liang Sicheng, Liu Hang, Chen Hongwei, Lü MuHan. The Gut Microbiome and Sex Hormone-Related Diseases. Frontiers in Microbiology.Vol. 12 2021. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2021.711137 Tang WH, Kitai T, Hazen SL. Gut Microbiota in Cardiovascular Health and Disease. Circ Res. 2017 Mar 31;120(7):1183-1196. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.309715. PMID: 28360349; PMCID: PMC5390330. Vivarelli S, Salemi R, Candido S, Falzone L, Santagati M, Stefani S, Torino F, Banna GL, Tonini G, Libra M. Gut Microbiota and Cancer: From Pathogenesis to Therapy. Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jan 3;11(1):38. doi: 10.3390/cancers11010038. PMID: 30609850; PMCID: PMC6356461. Fujimura KE, Lynch SV. Microbiota in allergy and asthma and the emerging relationship with the gut microbiome. Cell Host Microbe. 2015 May 13;17(5):592-602. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.04.007. PMID: 25974301; PMCID: PMC4443817. Nagao-Kitamoto H, Kitamoto S, Kuffa P, Kamada N. Pathogenic role of the gut microbiota in gastrointestinal diseases. Intest Res. 2016 Apr;14(2):127-38. doi: 10.5217/ir.2016.14.2.127. Epub 2016 Apr 27. PMID: 27175113; PMCID: PMC4863046. Wang R, Tang R, Li B, et al. Gut microbiome, liver immunology, and liver diseases. Cell Mol Immunol 2021;18(1):4-17. Medical Disclaimer: The information included on this blog is for educational purposes only. It is not intended nor implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice. The reader should always consult his or her healthcare provider to determine the appropriateness of the information for their own situation or if they have any questions regarding a medical condition or treatment plan. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this blog! Reading the information on this blog does not create a physician-patient relationship. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
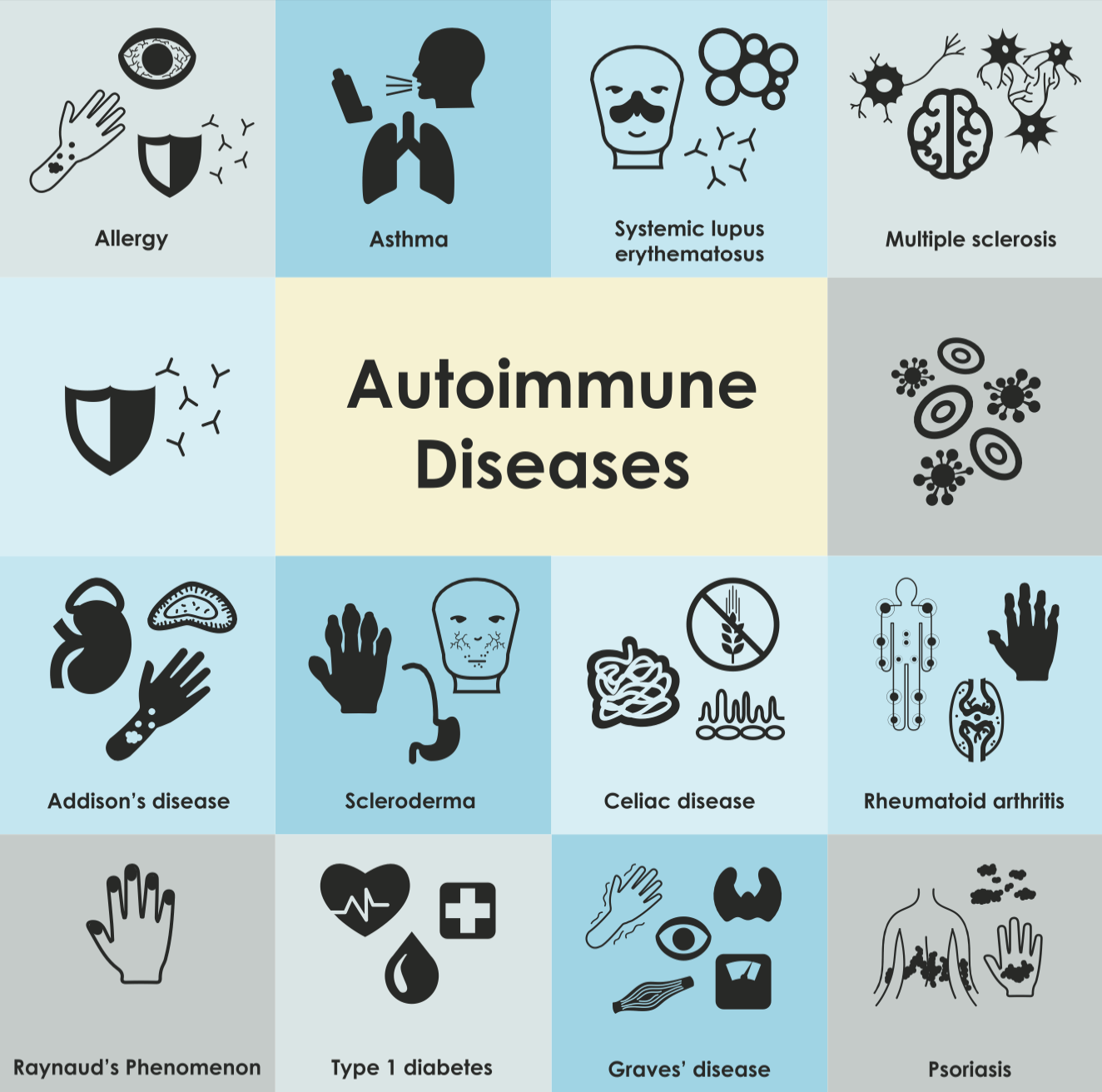
01 Aug, 2022
Have you ever wondered why, despite our best efforts to eat healthily and take care of ourselves, some people still develop autoimmune conditions? Or why two people with the same diagnosis can have vastly different symptoms? The answer lies in the unique way that each of us experiences the autoimmune process. With the help of Functional Medicine and Genomics, we can now begin to reframe the autoimmune process in a more individualized way. In this blog post, we will explore how Functional Medicine and Genomics can help us understand and treat our unique autoimmune conditions. Autoimmune conditions are on the rise. It is estimated that autoimmune diseases affect over 50 million Americans. That’s one in every six people! And while the exact cause of autoimmune conditions is still unknown, we do know that they are complex and often involve a combination of environmental and genetic factors. What is an autoimmune condition? Simply put, it is a condition in which your immune system mistakenly attacks your healthy tissues. This can happen for a variety of reasons, but most often it is because the body cannot distinguish between foreign invaders (like bacteria or viruses) and healthy cells. When this happens, the immune system produces antibodies that attack and destroy the healthy tissue. Autoimmune conditions can affect any part of the body, and they often result in a wide range of symptoms. Celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, lupus, thyroid disease, and Crohn's disease are just a few examples of autoimmune diseases. Both the gut and the genome have distinct immunological reactions that are unique to each individual, resulting in over a hundred different types of autoimmune diseases. Functional Medicine So how can Functional Medicine and Genomics help us reframe the autoimmune process? Functional Medicine is an approach to healthcare that focuses on finding the root cause of disease. Rather than simply treating symptoms, Functional Medicine practitioners look for underlying imbalances that may be contributing to illness. Gut health microbiota, for example, has been linked to autoimmune diseases. When the gut is out of balance, the immune system can go into overdrive trying to protect the body against perceived threats. This can lead to chronic inflammation and an increased risk of autoimmune disease. Genomics The human genome is the complete set of genetic instructions for a person. It is the blueprint for living. In recent years, advances in DNA sequencing technology have made it possible to map an individual's entire genome. This has given rise to the field of Genomic Medicine, which is using this information to develop more personalized approaches to healthcare. In the case of autoimmune conditions, Genomic Medicine can help us understand why some people are more susceptible to these diseases than others. For example, HLA, IL23R, TNFAIP3, and IL2RA genes have been connected to an increased risk of autoimmune illnesses. We can take preventative measures against autoimmune diseases by learning about our genetic make-up and implementing preventative strategies. We can also study how our genes interact with our environment to influence the development of autoimmune conditions. Learning about someone's DNA allows us to develop more tailored and efficient therapies for these problems. Knowing your genomic vulnerabilities allows you to take a proactive approach toward greater health. Conclusion Functional Medicine and Genomics are powerful tools that can help us understand our own unique experiences of the autoimmune process. By reframing the way we think about autoimmune conditions, we can begin to find more effective ways to treat and prevent them. This holistic approach often involves looking at the body as a whole system, rather than isolated parts. If you want to learn more about how Functional Medicine and Genomics may assist you on your health and wellness journey, talk with a Functional Medicine Provider that specializes in Genomics . If you'd like to learn more about autoimmune diseases, gut health, and Genomics, I've just released a book entitled " Understanding Genomics : How Nutrition, Supplements, and Lifestyle Can Help You Unlock Your Genetic Superpowers." This book is a must-read if you want to learn how to control your genetic destiny! Order a copy today ! Until then, stay healthy and happy! Dr. Marios Michael https://www.drmichaelswellness.com Resources: Dr. Marios Michael, DC, CNS, cFMP, 06/2022, Understanding Genomics; How Nutrition, Supplements, and Lifestyle Can Help You Unlock Your Genetic Superpowers, 1st edition, Austin, Bookbaby. Mazzone, R., Zwergel, C., Artico, M. et al. The emerging role of epigenetics in human autoimmune disorders. Clin Epigenet 11, 34 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-019-0632-2 Surace Anna Elisa Andrea, Hedrich Christian M. Role of Epigenetics in Autoimmune/Inflammatory Disease.Frontiers in Immunology. Vol. 10, 2019 DOI=10.3389/fimmu.2019.01525 Xu H, Liu M, Cao J, Li X, Fan D, Xia Y, Lu X, Li J, Ju D, Zhao H. The Dynamic Interplay between the Gut Microbiota and Autoimmune Diseases. J Immunol Res. 2019 Oct 27;2019:7546047. doi: 10.1155/2019/7546047. PMID: 31772949; PMCID: PMC6854958. Fasano A. Leaky gut and autoimmune diseases. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2012;42(1):71-78. doi: 10.1007/s12016-011-8291-x . Yamamoto K, Okada Y. Shared genetic factors and their causality in autoimmune diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(11):1449-1451. doi: 1136/annrheumdis-2019-215099 Medical Disclaimer: The information included on this blog is for educational purposes only. It is not intended nor implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice. The reader should always consult his or her healthcare provider to determine the appropriateness of the information for their own situation or if they have any questions regarding a medical condition or treatment plan. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this blog! Reading the information on this blog does not create a physician-patient relationship. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.

28 Jul, 2022
If you're looking for an excuse to travel to Europe, look no further than the Mediterranean diet! This delicious and healthy way of eating is popular all over the world, but it's most commonly found in countries like Italy, Greece, and Spain. So what is the Mediterranean diet? It's a way of eating that emphasizes fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, legumes, fish, and olive oil. In this blog post, we'll teach you how to eat like a local in one of these amazing countries. We'll also give you some tips on how to make the Mediterranean diet work for you! The Mediterranean diet is all about fresh, seasonal ingredients. That means that you'll want to start by seeking out the freshest fruits and vegetables that are in season. Head to your local farmer's market or grocery store and stock up on whatever looks good! tomatoes, eggplant, zucchini, garlic, onions, peppers, lemons, and oranges are all great options. Once you have your produce, it's time to start cooking! One of the best things about the Mediterranean diet is that it's incredibly versatile. There are so many different ways to prepare fruits and vegetables, so you can never get bored. One of our favorite ways to cook veggies is to roast them in the oven. This brings out their natural sweetness and makes them extra delicious. Another great option is to grill your veggies on the barbecue. This is a popular way to cook in the Mediterranean, and it's perfect for summertime. Of course, no meal is complete without some protein. The Mediterranean diet typically relies on fish as its main source of protein. This is great news for seafood lovers, but what if you're not a fan of fish? Don't worry - there are plenty of other options. Chicken, lamb, and beef are all commonly eaten in the Mediterranean. If you're looking for a vegetarian option, tofu and tempeh make great substitutes for meat. Last but not least, no Mediterranean meal is complete without a little bit of olive oil. This healthy fat is a key component of the diet, and it's what gives many dishes their signature flavor. However, a good rule of thumb is to use olive oil for flavor, not for cooking. When olive oil is heated at high temperatures, it will smoke and become unpleasantly bitter. Instead, use it to finish a dish by drizzling it over the top after it's already cooked. According to recent research, the Mediterranean diet is our DNA's and Genome's favorite diet. It has been linked to a decreased risk of heart disease, stroke, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, depression, and cancer. It has also been found to improve cognitive function, memory, and even a longer life span! It should come as no surprise that the Mediterranean diet has won numerous accolades and is regarded by US News & World Report to be the "No. 1 Best Overall Diet" for the fifth year in a row. The Mediterranean diet is a delicious and healthy way of eating that can be enjoyed by everyone. Following the tips in this blog post, it will ensure that you're getting the most health benefits possible. And when it comes to dressing your salad, simple olive oil and vinegar combination is all you need. Be sure to use a good quality extra virgin variety. Trust us, you'll love it! Now that you know how to eat like a local in the Mediterranean, it's time to start planning your trip! This region has so much to offer, from stunning beaches to ancient ruins. And of course, the food is not to be missed. So what are you waiting for? Start packing your bags - and don't forget your sunscreen! Do you have any favorite Mediterranean recipes? We'd love to hear from you in the comments below! If you want to learn more about the Mediterranean diet check out chapter #5 of my new book " Understanding Genomics ; How Nutrition, Supplements, and Lifestyle Can Help You Unlock Your Genetic Superpowers." This book is a must-read if you want to learn how to control your genetic destiny! Order a copy today! Until then, stay healthy and happy! Dr. Marios Michael drmichaelswellness.com Resources: Dr. Marios Michael, DC, CNS, cFMP, 06/2022, Understanding Genomics; How Nutrition, Supplements, and Lifestyle Can Help You Unlock Your Genetic Superpowers, 1st edition, Austin, Bookbaby. Gwynne M, Mounsey A. Mediterranean diet: higher fat but lower risk. J Fam Pract. 2013 Dec;62(12):745-8. PMID: 24340336; PMCID: PMC3891943. Fitó M, Konstantinidou V. Nutritional Genomics and the Mediterranean Diet's Effects on Human Cardiovascular Health. Nutrients. 2016 Apr 13;8(4):218. doi: 10.3390/nu8040218. PMID: 27089360; PMCID: PMC4848687. Boccardi V, Esposito A, Rizzo MR, Marfella R, Barbieri M, Paolisso G. Mediterranean diet, telomere maintenance and health status among elderly. PLoS One. 2013 Apr 30;8(4):e62781. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062781. PMID: 23646142; PMCID: PMC3640022. Visioli F, Galli C. The role of antioxidants in the Mediterranean diet. Lipids. 2001;36 Suppl:S49-52. doi: 10.1007/s11745-001-0682-z. PMID: 11837993. https://www.usnews.com/info/blogs/press-room/articles/2022-01-04/u-s-news-reveals-best-diet-rankings-for-2022 Medical Disclaimer: The information included on this blog is for educational purposes only. It is not intended nor implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice. The reader should always consult his or her healthcare provider to determine the appropriateness of the information for their own situation or if they have any questions regarding a medical condition or treatment plan. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this blog! Reading the information on this blog does not create a physician-patient relationship. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.

28 Jul, 2022
Have you ever stopped to think about the implications of your thoughts? What if our thoughts left behind genetic markers? Well, it turns out that this is true! In a recent study, scientists found that when we have strong emotional reactions to something, it leaves a "memory" in our genes. This means that our thoughts can change our DNA! So what does this mean for you? Well, it's important to be aware of the power of your thoughts and how they can affect your health and well-being. We are what we think It has been said that we are what we think! If this is true, then our thoughts must leave some sort of mark on our DNA. And according to recent research, this may be the case. Scientists have found that certain thoughts and emotions can change the way our DNA is expressed. This process is known as “Epigenetics” and it refers to the way our environment can affect the way our genes are expressed. Epigenetics is a relatively new field of study, but it is already providing us with some incredible insights into how our thoughts and emotions can impact our health. Epigenetic DNA markings resemble a barcode and are literally above our genes, and every time we think, it's like scanning that barcode. Genes are the recipe for life. If we think good thoughts, it's similar to adding healthy ingredients to our recipe. On the other hand, if we think negative thoughts, it's like adding toxins and poison to our recipe. So what does this mean for you? Well, if you're constantly thinking negative thoughts, your DNA is going to reflect that. On the other hand, if you're constantly thinking positive thoughts, your DNA will reflect that as well. So what we think does matter! Take a moment to pause and focus on your breath the next time you're stressed or anxious. And remember, you have the power to change your DNA! Emotional Trauma For example, one study found that people who experienced emotional trauma in their lives had changes in their DNA that were passed down to their children. This means that the effects of trauma can actually be passed down through generations! Fear According to research fear can affect our DNA. The study found that people who were exposed to a lot of fear had changes in their DNA that made them more likely to experience anxiety and depression. A different study showed that fear can be passed on to future generations. Meditation Another study found that people who meditated had changes in their DNA that were associated with better health and well-being. These findings show us that our thoughts and emotions can have a very real impact on our genetic material. Conclusion In truth, no mind-body event is disconnected; thus genetics has been challenged. Our DNA is no longer fixed and sealed away; instead, it is dynamic and active. With each idea, word, and action you engage in, you're communicating with your genes. Experiences are recorded and remembered at the genetic level. So what does this all mean for you? It means that your thoughts and emotions can influence your health and the health of your future children. It's important to be aware of the power of your thoughts and how they can affect your health and well-being. If you're going through a tough time, don't hesitate to reach out for help. And if you want to improve your health, consider incorporating some mindfulness into your daily routine. The power of your thoughts is more than just a saying, it's science! Here are some things to keep in mind: -Your thoughts leave genetic footprints -Your thoughts can influence your genes. -Your thoughts can impact your health and well-being. -Your thoughts and emotions can influence the health of your future children. -You have the power to change your DNA expression with your thoughts. -You have the power to change your health, your appearance, and even your destiny. This is just a brief overview of what our thoughts can do to our DNA. If you want to learn more, check out my new book "Understanding Genomics; How Nutrition, Supplements, and Lifestyle Can Help You Unlock Your Genetic Superpowers." This book is a must-read if you want to learn how to control your genetic destiny! Order a copy today! Until then, stay healthy and happy! Dr. Marios Michael drmichaelswellness.com Resources: Dr. Marios Michael, DC, CNS, cFMP, 06/2022, Understanding Genomics; How Nutrition, Supplements, and Lifestyle Can Help You Unlock Your Genetic Superpowers, 1st edition, Austin, Bookbaby. Dora L. Costa,Noelle Yetter, and Heather DeSome, Intergenerational transmission of paternal trauma among US Civil War ex-POWs, October 15, 2018, 115 (44) 11215-11220 https://doi.org/pnas.1803630115 Feder A, Nestler EJ, Charney DS. Psychobiology and molecular genetics of resilience. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009 Jun;10(6):446-57. doi: 10.1038/nrn2649. PMID: 19455174; PMCID: PMC2833107. The Power of Thought: Our Thoughts Leave Genetic Marks, What This Means for You | The Chopra Center https://chopra.com/articles/how-your-genes-can-make-you-happier. https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/the-right-mindset/202002/five-thought-patterns-may-hurt-your-dna. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/fearful-memories-passed-down/ https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/how-parents-rsquo-trauma-leaves-biological-traces-in-children/. Your Thoughts Can Literally Change The Expression Of Your Genes | Bruce Lipton Ph.D. Gapp, K., van Steenwyk, G., Germain, P.L. et al. Alterations in sperm long RNA contribute to the epigenetic inheritance of the effects of postnatal trauma. Mol Psychiatry 25, 2162–2174 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0271-6 Ali Jawaid, Katherina-Lynn Jehle, Isabelle M. Mansuy, Impact of Parental Exposure on Offspring Health in Humans, Trends in Genetics, 37, 4, (373-388), (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2020.10.006 Medical Disclaimer : The information included on this blog is for educational purposes only. It is not intended nor implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice. The reader should always consult his or her healthcare provider to determine the appropriateness of the information for their own situation or if they have any questions regarding a medical condition or treatment plan. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this blog! Reading the information on this blog does not create a physician-patient relationship. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.

28 Jul, 2022
Did you know that there are trillions of bacteria living inside of you? These bacteria make up your microbiome, and they play a huge role in keeping you healthy! In this blog post, we will discuss the microbiome and how it affects your health. We will also talk about the benefits of having a healthy microbiome. So, if you're interested in learning more about the trillions of bacteria that keep you alive, keep reading! What is it? The microbiome is a hot topic in science these days. And for good reason - we're only just beginning to understand the role that trillions of bacteria play a crucial role in keeping us healthy. The microbiome is the collection of all microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and viruses, that reside on and in our bodies. The majority of them live in the gut. DNA studies have found that we have more bacterial DNA than human DNA.- our bodies are home to around 100 trillion bacteria, compared to the mere 30 trillion human cells. These tiny organisms outnumber human cells by a factor of ten to one. These bacteria are found in your gut, on your skin, and in other places. Most of them are harmless, and some are even beneficial. The microbes in our gut alone weigh about as much as our brain! We couldn't survive without them! What does it do? There are many different types of bacteria in the microbiome. Some of these bacteria are good for you and some of them are bad for you. You can have a healthy microbiome or an unhealthy microbiome. A healthy balanced microbiome boosts the immune system, protects against pathogenic bacteria, and helps with the management of IBS, Chron's Disease, and Ulcerative Colitis. It aids in weight loss, extends lifespan, protects against infections, produces vitamins like K, and B12, as well as enzymes, and breaks down food. These bacteria even influence our mood and mental health! There are many functions of the microbiome that we are only just beginning to understand. An unhealthy microbiome can lead to weight gain, skin problems, allergies, autoimmune conditions, and even mental health issues. It can also make you more susceptible to infections, diseases, and cancer. So, it's important to keep your microbiome healthy! How do you do that? How do I get a healthy microbiome? There are many things that you can do to get and keep your microbiome healthy. For example, you can take prebiotic, probiotic, and postbiotic supplements. Prebiotics are a type of fiber that serves as food for the probiotics (beneficial bacteria) in your gut. Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that are good for your health, especially your digestive system. Postbiotics are compounds produced by probiotics during fermentation. Butyrate, for example, is a postbiotic that helps reduce inflammation, builds and strengthens the gut barrier function, and has even been shown to have anti-cancer effects. You may reduce your risk of having an unhealthy microbiome by not taking antibiotics unless necessary. Always check with your physician before stopping any medication. Probioplex ® Intensive Care is one of the popular Practitioner-Grade Prebiotic formulas. According to Metagenics, Probioplex ® Intensive Care is an innovative formula produced by a temperature/pH-controlled micro-filtration process that yields biologically active immunoglobulins. These immunoglobulins support healthy intestinal immune activity. In addition, Probioplex Intensive Care supplies lactoferrin and lactoperoxidase, proteins that support intestinal health, and friendly bacteria such as lactobacilli and bifidobacteria. When choosing a probiotic supplement, it is important to choose one that contains live, active cultures. The number of live bacteria in a supplement can vary from product to product. It is also important to make sure the supplement you choose has been tested for safety and effectiveness. Quality matters when it comes to probiotic supplements, so be sure to choose a reputable brand or a Practioner- Grade product A balanced diverse microbiome is of utmost importance. Eating a varied diet rich in Fructooligosaccharides (FOS) such as onions, chicory, garlic, asparagus, bananas, and artichokes among many others can help promote the growth of healthy gut bacteria. You can also maintain a healthy microbiome by eating a diet that is high in fiber and low in sugar. Fermented foods, such as yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, and pickles, can also help you keep a healthy gut flora. The Mediterranean diet has been shown to promote a healthy microbiome. This diet is high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and olive oil. It also includes moderate amounts of fish, poultry, and red wine. So if you're looking to maintain a healthy microbiome, eating a Mediterranean diet is a good place to start! In addition to a healthy diet, there are other things you can do to keep your microbiome healthy such as exercise regularly, getting enough sleep, and managing stress. Conclusion The microbiome is unique to each individual, and it changes throughout our lifetime. Factors such as diet, medications, stress, and exposure to toxins can all impact the health of our microbiome. By taking care of your microbiome, you’re not only supporting your health, but also the health of the trillions of microbes that call your body home. This is a brief introduction to our microbiome. I hope you find it interesting. If you want to learn more about gut health and the microbiome, I've written a new book called " Understanding Genomics : How Nutrition, Supplements, and Lifestyle Can Help You Unlock Your Genetic Superpowers." This book is a must-read if you want to learn how to control your genetic destiny! Order a copy today! Until then, stay healthy and happy! Dr. Marios Michael drmichaelswellness.com Resources: Dr. Marios Michael, DC, CNS, cFMP, 06/2022, Understanding Genomics; How Nutrition, Supplements, and Lifestyle Can Help You Unlock Your Genetic Superpowers, 1st edition, Austin, Bookbaby. Quigley EM. Gut bacteria in health and disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2013 Sep;9(9):560-9. PMID: 24729765; PMCID: PMC3983973. https://doi.org/pnas.1803630115 Ing Yang1,2,3†, Ji Pu1,2†, Shan Lu1,2,3†, Xiangning Bai1, Yangfeng Wu4, Dong Jin1,2,3, Yanpeng Cheng1, Gui Zhang1, Wentao Zhu1, Xuelian Luo1, Ramon Rosselló-Móra5 and Jianguo Xu1,2,3. Species-Level Analysis of Human Gut Microbiota With Metataxonomics, Front. Microbiol., 26 August 2020 https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2020.02029/full Sabater-Molina M, Larqué E, Torrella F, Zamora S. Dietary fructooligosaccharides and potential benefits on health. J Physiol Biochem. 2009 Sep;65(3):315-28. doi: 10.1007/BF03180584. PMID: 20119826. https://www.metagenics.com Jin Q, Black A, Kales SN, Vattem D, Ruiz-Canela M, Sotos-Prieto M. Metabolomics and Microbiomes as Potential Tools to Evaluate the Effects of the Mediterranean Diet. Nutrients. 2019; 11(1):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010207 Medical Disclaimer : The information included on this blog is for educational purposes only. It is not intended nor implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice. The reader should always consult his or her healthcare provider to determine the appropriateness of the information for their own situation or if they have any questions regarding a medical condition or treatment plan. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this blog! Reading the information on this blog does not create a physician-patient relationship. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.


